Welcome to an introduction of the Atkins Diet! The Atkins Diet is a popular low-carb diet that focuses on controlling your intake of carbohydrates to help you lose weight and improve your overall health. The core principles of the Atkins Diet include reducing your carb intake, consuming healthy fats and proteins, and gradually reintroducing carbs in phases. Keep reading to learn more about how the Atkins Diet can change your approach to nutrition and lead to successful weight loss.
What Is The Atkins Diet And What Are Its Core Principles?
Are you confused about the Atkins Diet and what it entails? Let’s break it down for you in simple terms so you can have a better understanding of this popular weight-loss method.
Understanding the Atkins Diet
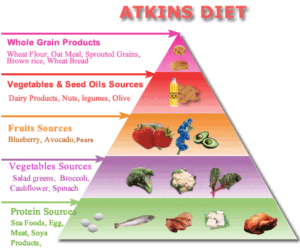
The Atkins Diet is a low-carbohydrate diet that aims to promote weight loss by limiting the intake of carbohydrates and increasing the consumption of proteins and fats. This approach is based on the idea that reducing carbs can force the body to burn stored fat for energy, resulting in weight loss.
The diet was created by Dr. Robert Atkins in the 1970s and has since gained widespread popularity as a way to shed pounds without feeling deprived or hungry. It has evolved over the years and now offers different plans to suit individual needs and preferences.
Now, let us discuss the variations of the Atkins diet plan;
Atkins 20
- You restrict your daily carbohydrate intake to 20 grams.
- It is designed for those who want to achieve rapid weight loss by inducing ketosis, a state where your body burns fat for energy.
- Suffering from prediabetes or type 2 diabetes.
Atkins 40
- Here, you have a daily carbohydrate limit of 40 grams, making it flexible to achieve weight loss.
- You get the variety of food choices required in the Atkins diet plan.
- Suitable for pregnant and breastfeeding women.
Atkins 100
- Permits up to 100 grams of carbohydrates daily.
- It helps you lose weight slowly and gradually, and you learn about healthy eating habits.
- It also helps you maintain your current weight.
All the variations of the Atkins diet plan offer a unique approach to achieving a calorie deficit diet, allowing you to tailor your diet to your specific weight loss goals and preferences while maintaining nutritional quality.
The Four Phases of the Atkins Diet
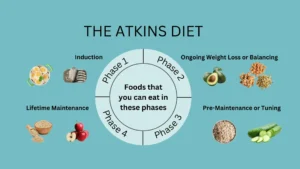
The Atkins Diet is divided into four phases, each with its own specific guidelines and objectives. Let’s take a closer look at what each phase entails:
Phase 1: Induction
In this initial phase, you are required to restrict your carbohydrate intake to 20-25 grams per day. This is meant to kickstart the process of fat burning by putting your body in a state of ketosis. During this phase, you are encouraged to focus on consuming high-fat, high-protein foods while avoiding starchy carbs like bread, pasta, and sugar.
What do you eat in this phase?
- Protein: You can consume various protein sources, such as meat (like beef, pork, poultry), fish, and eggs.
- Healthy Fats: Include fats like olive oil, coconut oil, and avocados.
- Low-Carb Vegetables: You can eat non-starchy vegetables like spinach, kale, and broccoli. To this end, you can introduce low carb breakfast recipes, a delicious and healthy way to start your day while maintaining your dietary goals.
- Cheese: Some cheese is allowed, but it’s essential to monitor portion sizes.
What is restricted in this phase?
- Carbohydrates: Carbohydrates are significantly prohibited, so avoid foods like bread, pasta, rice, and most fruits.
- Sugar: All forms of sugar and sugary foods are restricted.
- High-Starch Vegetables: Vegetables like potatoes, corn, and carrots, which are high in starch, are limited.
- Legumes: Foods like beans, lentils, and peas are restricted due to their carbohydrate content.
- Processed Foods: Highly processed foods are generally discouraged.
What Happens in your body during this phase?
According to a research by escholarship, this is the stage when the body’s metabolism process shifts. Two new metabolic processes begin at this stage: lipolysis (burning fat for fuel) and ketosis (converting fatty acids to ketones for energy, the surplus of which is excreted in the urine).
Tips To Have A Safer Phase 1;
- Choose Quality Proteins: Opt for lean and high-quality protein sources to support your dietary goals and overall health.
- Keep track of your carbohydrate intake: Learn about net carbs and how to calculate them using the convenient carb counter alongside the Atkins diet food list for your specific plan.
- Have three meals and two snacks in a day: Plan your meals a day before, but never stay hungry for more than four hours.
- Drink plenty of water.
- Monitor Electrolytes: Be mindful of your electrolyte balance, especially sodium, potassium, and magnesium.
Phase 2: Balancing
Once you have successfully completed the Induction phase, you can gradually add more nuts, seeds, and low-carb vegetables back into your diet. The goal is to find your “Critical Carbohydrate Level for Losing” (CCLL), which is the maximum amount of carbs you can consume while still losing weight.
What do you eat in this phase?
- Protein: All meats, poultry, seafood, and eggs.
- Healthy Fats: Avocados, nuts, seeds, olive oil, coconut oil
- Limited fruits: Cantaloupe, honeydew, melons, etc.
You can re-introduce carbs in the following sequence;
- Nuts and seeds, nut and seed butter and nut and seed flour
- Berries, cherries and melon (but not watermelon)
- Plain, unsweetened whole-milk yoghurt, cottage cheese and ricotta
- Legumes such as chickpeas, lentils, etc.
- Tomato and vegetable juice.
What is restricted in this phase?
- High-carb fruits: Bananas, apples, oranges, pears, grapes, etc.
- Starchy vegetables: Potatoes, corn, sweet potatoes, carrots, etc.
- Legumes: Beans, lentils, peas, etc.
- Added sugar: Soft drinks, fruit juices, candy, desserts, etc.
- Processed foods: Anything in a box or bag is likely high in carbs and unhealthy ingredients.
What Happens in your body during this phase?
The goal of Phase 2 is to find your personal carb tolerance, which is the maximum amount of carbs that you can eat each day without gaining weight. This can vary from person to person, so it is important to experiment to find what works best for you.
Tips For Healthy Weight Loss In Phase 2;
- Introduce more variety, not more food.
- Continue to consume a minimum of 12–15 daily grams of net carbs as foundation vegetables.
- Increase your overall daily net carb intake; this can be done in 5-gram increments every week.
Phase 3: Pre-Maintenance
At this stage, you are close to reaching your weight loss goal. You can start introducing more carbs into your diet, such as fruits, whole grains, and legumes, while monitoring your weight to find the right balance between carbs and weight maintenance.
What do you eat in this phase?
- Protein: All meats, poultry, and seafood. Eggs, Tofu, tempeh and Legumes (beans, lentils, peas) in moderation.
- Healthy fats: Avocados, Nuts and seeds, Olives and olive oil, Coconut oil and Fatty fish like salmon and tuna
- Low-carb vegetables: Leafy greens, Broccoli, Cauliflower, Asparagus, Cabbage, Zucchini, Eggplant and more.
- Starchy vegetables (in small amounts): Potatoes, corn, sweet potatoes, carrots, etc.
- Low-glycemic index (GI) fruits: Berries, Apples, Pears, Citrus fruits, Melons
- Whole grains: Brown rice, Quinoa, Whole-wheat bread and pasta, Oats, etc.
- Dairy: Full-fat cheese, Yoghurt, Milk, Kefir
What is restricted in this phase?
- Added sugar: Soft drinks, fruit juices, candy, desserts, etc.
- Processed foods: Anything in a box or bag is likely high in carbs and unhealthy ingredients.
- Trans fats: Fried foods, processed meats, etc.
- High-carb fruits: Bananas, apples, oranges, pears, grapes, etc.
What Happens in your body during this phase?
Phase 3 of the Atkins diet plan is a transition phase that aims to help you maintain your weight loss while gradually reintroducing carbohydrates. During this phase, your body continues to adapt to burning fat for energy and adjust to the new level of carbohydrate intake.
The digestive system adapts to processing the increased carbohydrate intake. Gut bacteria, which contribute to nutrient absorption and metabolism, also adjust to the new dietary composition.
Tips for Phase 3
- You need to try a variety of carbs, recipes and dishes to figure out which of them could be the best for the long run. You have to keep the count of your using a food calorie calculator, especially that of foods rich in carbs.
- You can gradually increase your carbohydrate intake by 10 grams each week, up to 100 grams, to determine the right balance.
- Incorporate legumes, starchy vegetables, a greater variety of fruits, and grains into your diet.
- Plan your meals ahead of time. This will help you to make healthy choices and avoid temptation.
Phase 4: Maintenance
Once you have reached your desired weight, you can transition into the Maintenance phase, where you can consume a wider variety of foods in moderation while keeping an eye on your carbohydrate intake. This phase is designed to help you sustain your weight loss in the long term.
What do you eat in this phase?
The foods that you experimented with in Phase 3 are to be consumed similarly. But, by now, you’ve learned about foods that work for your body and boost metabolism so that you can make suitable changes in your diet. For convenience, consider using this Atkins diet food list;
- Protein: Good protein sources include lean meats, poultry, fish, eggs, legumes, and tofu.
- Healthy fats: Include healthy fats from sources like avocados, nuts, seeds, olive oil, and fatty fish.
- Nuts and Seeds: Enjoy small portions of nuts and seeds.
- Gradually reintroduce whole grains into your diet.
- Prioritise whole, unprocessed foods: Emphasize the importance of eating whole, unprocessed foods that are nutrient-rich and naturally low in sugar and unhealthy fats.
What is restricted in this phase?
In Phase 4 of the Atkins diet plan, restrictions are generally less stringent than in the earlier phases, but it’s important to maintain a balance and monitor your carbohydrate intake.
What Happens in your body during this phase?
During Phase 4 of the Atkins diet, your body continues to adapt to the new balance of carbohydrates, fats, and proteins in your diet. This phase is designed to help you maintain your weight loss and overall health for the long term.
Tips for Phase 4
- Keep consuming at least 12–15 grams of Net Carbs from foundation vegetables.
- Maintain your protein intake at 4–6 ounces of cooked protein per meal.
- Aim to have healthy snacks like fruits twice a day.
- Calculate your food calories and carbohydrates at least once a week using devices like the daily calorie intake calculator and carbs calculator, respectively.
Food Guidelines on the Atkins Diet
The Atkins Diet emphasizes the importance of choosing high-quality, nutrient-dense foods while limiting processed and refined carbohydrates. Here are some guidelines to follow when it comes to food choices:
Foods to Eat
- Proteins: Include sources like meat, fish, poultry, eggs, and tofu in your meals to help you feel full and satisfied.
- Healthy Fats: Opt for foods rich in healthy fats such as avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil to provide energy and support overall health.
- Low-Carb Vegetables: Load up on non-starchy vegetables like leafy greens, broccoli, and cauliflower for essential vitamins and minerals.
- Fruits: Stick to lower-sugar fruits like berries, apples, and citrus fruits in moderation to satisfy your sweet tooth.
Foods to Avoid
- Sugar: Steer clear of sugary treats, sodas, and desserts that can spike blood sugar levels and sabotage your weight loss efforts.
- Processed Carbs: Avoid foods like white bread, pasta, and pastries that are high in refined carbohydrates and offer little nutritional value.
- Trans Fats: Say no to foods containing trans fats or hydrogenated oils, which can increase inflammation and affect heart health.
- Alcohol: Limit alcohol consumption, especially those high in sugar and carbs, to prevent hindering your progress on the diet.
Benefits of the Atkins Diet
Following the Atkins Diet can offer a range of benefits beyond just weight loss. Here are some of the positive effects you may experience when following this eating plan:
- Weight Loss: By restricting carbs and increasing fats and proteins, you may see significant weight loss results, especially in the initial phases of the diet.
- Improved Blood Sugar Control:As you continue to eat low-glycemic index (GI) carbohydrates, your body becomes more sensitive to insulin. Insulin is a hormone that helps your body to use glucose for energy. When you are insulin-sensitive, your body can use glucose more efficiently, and you are less likely to store excess glucose as fat.
- Appetite Suppression: High-protein foods can make you feel full and satisfied, reducing cravings and hunger pangs throughout the day.
- Increased Energy: Many people report feeling more energized and mentally sharp on the Atkins Diet due to the steady release of energy from fats and proteins.
- Better Overall Health: Following a low-carb, high-fat diet can lead to improvements in cholesterol levels, blood pressure, and inflammation markers in the body.
- Chronic Diseases: Two of the primary causes of fatal diseases like diabetes and cancer include a problem with blood pressure, cholesterol levels and hypertension. Consuming the Atkins diet meal plan, which directs you to eat low-carb foods, helps you treat these issues. Another major cause of chronic disorders is unhealthy body weight, which is treated in this meal plan. You learn to lose weight through sustainability.
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS): PCOS is a common hormonal disorder that affects females with ovaries. It can lead to irregular periods, ovarian cysts, and symptoms like acne and excess hair growth. The Atkins Diet plan can benefit individuals with PCOS in several ways. It may help control blood sugar, an essential aspect of managing PCOS. The initial phases of the diet can lead to weight loss, which is often recommended for PCOS management.
- Skin and Acne: The relationship between the Atkins Diet and acne is not fully understood, and individual responses may vary. Some people have reported improvements in acne while following a low-carb, high-protein diet like Atkins. Reducing refined sugars and processed foods in the diet may help stabilise blood sugar levels, which can be a factor in acne.
Potential Drawbacks of the Atkins Diet
While the Atkins Diet has its benefits, it’s essential to be aware of some potential drawbacks that may come with this eating plan:
- Nutrient Deficiencies: Cutting out certain food groups, especially whole grains and fruits, can lead to deficiencies in essential vitamins and minerals over time.
- Keto Flu: Some people may experience symptoms like fatigue, headaches, and irritability when transitioning to a low-carb diet, known as the “keto flu.”
- Digestive Issues: Increasing fat intake can cause digestive disturbances like constipation or diarrhea in some individuals until the body adapts to the new eating plan.
- Sustainability: The strict carb restrictions and limitations on certain foods may make it challenging for some people to stick with the Atkins Diet in the long run.
- Social Limitations: Following a low-carb diet can pose challenges when dining out or attending social events where high-carb foods are prevalent.
- Kidney Stones: The high protein intake and reduced carbohydrate intake of the Atkins diet may increase the risk of kidney stones. Increased protein metabolism produces more uric acid, a component of kidney stones. Additionally, the Atkins diet may cause dehydration, further increasing the risk of stone formation.
- Nutritional Deficiencies: The Atkins diet, particularly in its early phases, can restrict the intake of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, essential sources of vitamins, minerals, and fibre. Prolonged restriction of these nutrient-rich foods could lead to deficiencies in vitamins A, C, E, potassium, magnesium, and fibre.
Who Should Consider Trying the Atkins Diet?
The Atkins Diet may be suitable for individuals who are looking to lose weight, improve their metabolic health, or manage conditions like type 2 diabetes or metabolic syndrome. Here are some scenarios where the Atkins Diet may be worth considering:
- Weight Loss Goals: If you have struggled to lose weight on traditional low-fat diets, the Atkins Diet’s focus on fat and protein may be more effective for you.
- Blood Sugar Control: If you have insulin resistance, prediabetes, or type 2 diabetes, reducing carb intake can help stabilize blood sugar levels and improve insulin sensitivity.
- Metabolic Health: Individuals with metabolic syndrome, high cholesterol, or hypertension may benefit from the Atkins Diet’s ability to improve lipid profiles and blood pressure.
- Food Sensitivities: If you have sensitivities to gluten, grains, or certain carbohydrates, the Atkins Diet’s emphasis on whole foods and limiting carbs may help alleviate symptoms.
FAQs
Is Atkins Diet just keto?
No, the Atkins Diet plan and the ketogenic (keto) diet share similarities but are different. Both emphasise low carbohydrate intake, but the Atkins Diet has multiple phases, including gradually reintroducing carbs. At the same time, keto is typically more restrictive, with a constant focus on high fat intake.
How much weight can I lose on Atkins Diet?
Weight loss on the Atkins Diet varies from person to person. In the initial phases, some individuals can experience rapid weight loss due to reduced carbohydrate intake, but the rate of weight loss typically slows down as the diet progresses.
What is the best low carb diet for weight loss?
The best low-carb diet for weight loss depends on your preferences and needs. In addition to Atkins, other diets include the ketogenic diet, the Mediterranean diet (with reduced carbohydrates), and the South Beach Diet. The “best” diet is one that you can maintain in the long term and aligns with your health and weight goals.
Which fruits can I eat on Atkins diet?
In the later phases of the Atkins Diet plan, you can reintroduce fruits gradually. Opt for fruits that are lower in carbohydrates, such as berries (strawberries, blueberries, raspberries), melons (cantaloupe, watermelon), and avocados. These fruits are relatively lower in sugar and carbs compared to others.
Can I eat Yogurt on Atkins Diet?
Yes, yoghurt can be included in the Atkins diet plan, especially in the later phases. Opt for plain, unsweetened yoghurt to minimise added sugars. Greek yoghurt, which is higher in protein and lower in carbs, can be an excellent choice.
Can I eat Banana on Atkins Diet?
In the later phases of the Atkins diet plan, you can gradually reintroduce some fruits, including bananas, in moderation. However, bananas are relatively high in carbohydrates and sugars compared to other fruits, so it’s essential to monitor your carbohydrate intake and portion sizes.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Atkins Diet is a low-carb eating plan that focuses on reducing carbohydrate intake to promote weight loss and improve overall health. By following the four phases of the diet and adhering to the food guidelines provided, you can experience the benefits of this approach while being mindful of potential drawbacks.
Whether you choose to try the Atkins Diet or not, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider or nutritionist before making significant changes to your diet, especially if you have underlying health conditions or concerns. Remember that finding an eating plan that works for you and supports your unique needs and goals is key to long-term success and overall well-being.